Choosing the right suction pump can be a daunting task, especially with the myriad of options available on the market today. A suction pump is an essential tool used in various industries and applications, from medical settings to industrial processes, and selecting the appropriate type can significantly impact efficiency and productivity. Understanding the different styles, capacities, and materials available is crucial for ensuring that the suction pump you choose meets your specific needs.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the various suction pump types, their functionalities, and the critical factors to consider during the selection process. Whether you require a pump for fluid transfer, drainage, or even vacuum generation, this ultimate guide will equip you with the necessary knowledge to make an informed decision and choose the right suction pump that aligns with your requirements.
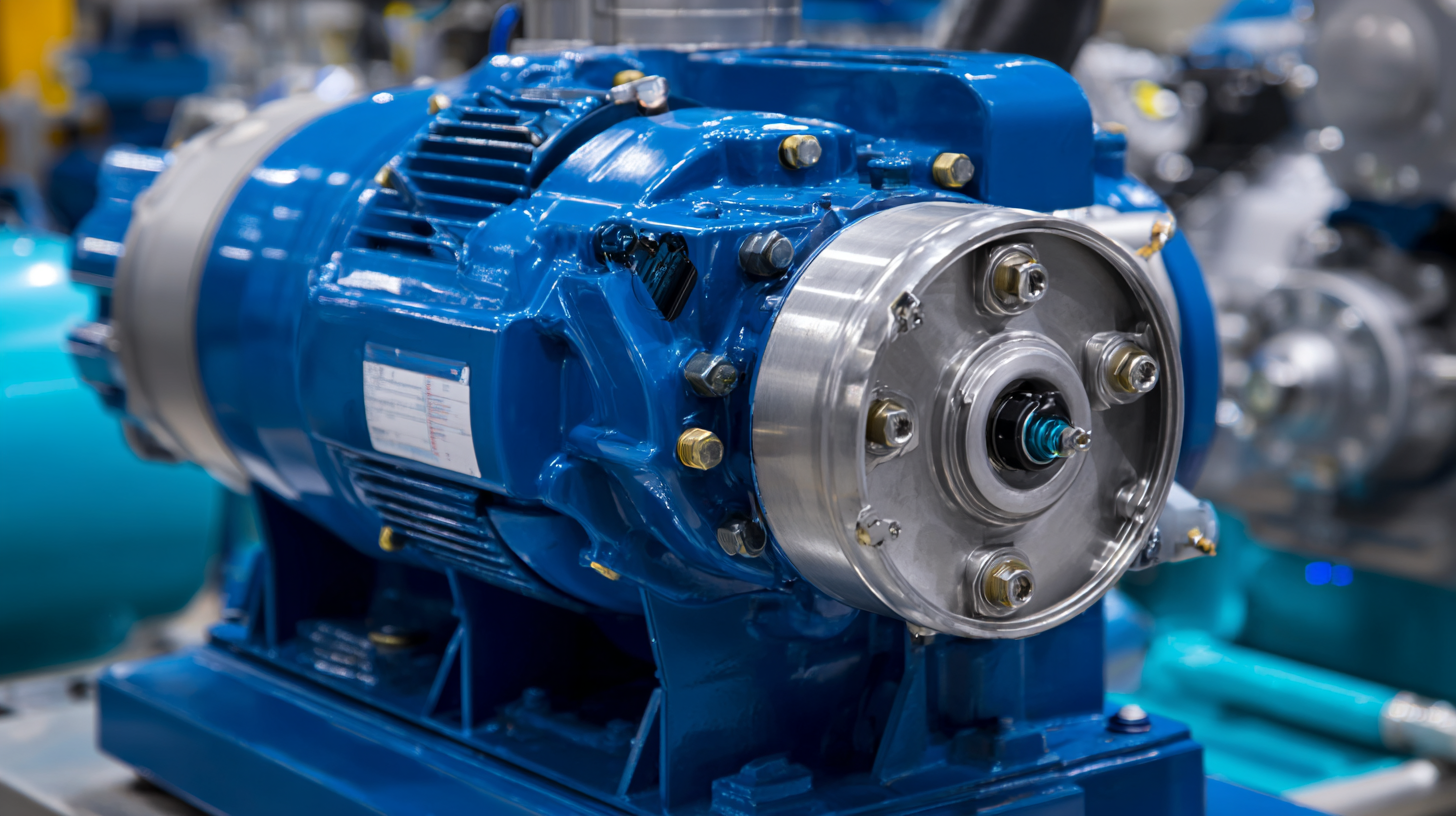

When selecting a suction pump, it’s crucial to understand the various types available and their specific applications. Centrifugal pumps are commonly used for transferring liquids, as they utilize a rotating impeller to generate flow. These pumps are ideal for moving large volumes of fluid quickly, making them suitable for agricultural irrigation and water supply systems. However, they may not be the best choice for viscous fluids or applications requiring high suction lift.
On the other hand, positive displacement pumps, including gear and diaphragm pumps, excel in handling thicker liquids and achieving high pressures. Gear pumps are often used in oil and fuel transfer due to their ability to deliver consistent flow rates, while diaphragm pumps are preferred in chemical and pharmaceutical industries for their ability to handle corrosive substances without leakage. Each type serves unique purposes, highlighting the importance of aligning the pump's characteristics with your specific needs for optimal performance and efficiency.
When selecting a suction pump, understanding key technical specifications is crucial to ensure optimal performance for your specific requirements. One of the most important factors to consider is the pump's flow rate, which indicates how much fluid the pump can move in a given period. This specification helps you determine if the pump can handle the volume of liquid you need to transfer efficiently. Additionally, checking the pump's maximum suction lift capabilities will reveal how deep it can draw fluid, which is particularly important if you are working in environments with varying fluid levels.
Another critical specification is the pump's material composition. Depending on the type of fluid being pumped—whether corrosive, viscous, or particulate-laden—the materials used in the pump must be compatible to avoid damage and ensure longevity. The power source of the pump is also vital; whether it is electric, gasoline, or air-operated, knowing the power requirements will help you select a pump that fits your operational setup. Together, these technical specifications will guide you towards making an informed choice when selecting the right suction pump for your needs.
| Specification | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Pump Type | The design of the pump used for suction. | Diaphragm, Centrifugal, Gear |
| Capacity | The volume of fluid the pump can handle, typically measured in liters per minute (LPM). | 5 - 100 LPM |
| Suction Lift | The maximum height the pump can lift the fluid. | 3 - 7 meters |
| Power Source | The energy type that drives the pump. | Electric, Gasoline, Manual |
| Material | The material used in the construction of the pump body and components. | Plastic, Stainless Steel, Aluminum |
| Noise Level | The sound produced by the pump during operation. | < 70 dB |
| Maintenance | Frequency and ease of upkeep required for optimal performance. | Monthly, Quarterly |
When evaluating pump efficiency, three key factors come to the forefront: flow rate, power consumption, and noise levels.
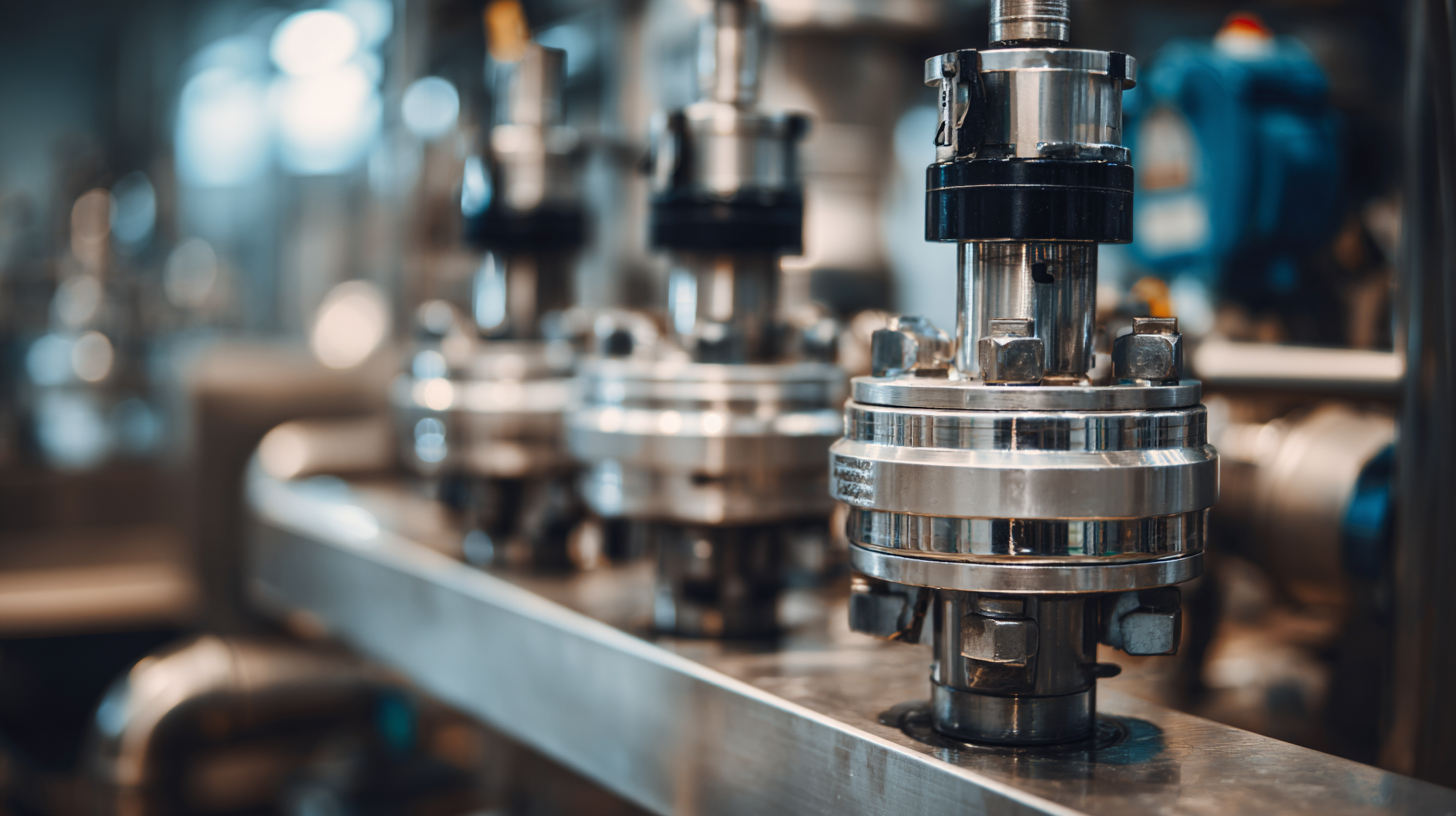 Flow rate essentially dictates the volume of fluid a pump can move, which directly impacts its performance in various applications. Selecting a pump with an optimal flow rate for your specific needs ensures that you achieve efficiency without overworking the motor or wasting energy.
Flow rate essentially dictates the volume of fluid a pump can move, which directly impacts its performance in various applications. Selecting a pump with an optimal flow rate for your specific needs ensures that you achieve efficiency without overworking the motor or wasting energy.
Power consumption is another crucial consideration. Energy-efficient pumps not only lower operational costs but also reduce the environmental impact of energy use. When choosing a pump, it’s essential to look for models that offer high performance while maintaining low power consumption. This balance facilitates better sustainability and cost savings over time.
Noise levels should not be overlooked, especially in environments where quiet operation is a priority. Many modern pumps incorporate technologies that minimize sound while maintaining performance. When assessing your options, consider models with noise reduction features to enhance the comfort and functionality of your space.
Tips:
- Always check for efficiency ratings and certifications.
- Compare different models and read user reviews to get insights on long-term performance.
- Consider the installation environment to choose a pump that minimizes noise and disruption.
When selecting a suction pump, one of the critical factors to consider is material compatibility, especially in environments prone to contamination, such as industrial zones. Recent studies, like the comparative analysis of heavy metals toxicity in drinking water in Gujranwala, Pakistan, highlight the significant impact that industrial activities have on environmental health. Heavy metals, if not properly managed, can corrode pump materials, leading to pump failures and contamination of the fluids being handled. A study by the World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes that exposure to heavy metals in drinking water can lead to severe health issues, underscoring the necessity of choosing the right materials that can withstand such harsh conditions.
Furthermore, evaluating the compatibility of pumps with different types of fluids, including brine and other chemically reactive substances, is essential. A recent case study on water injection compatibility in a Middle Eastern reservoir demonstrated that varying water quality can greatly affect scale formation and overall system efficiency. Utilizing materials that are resistant to scaling and corrosion not only prolongs the lifespan of the pump but also enhances the reliability of the entire system. Experts recommend materials such as high-quality stainless steel or special alloys for applications in aggressive environments, ensuring that the suction pump operates effectively and safely under all conditions.
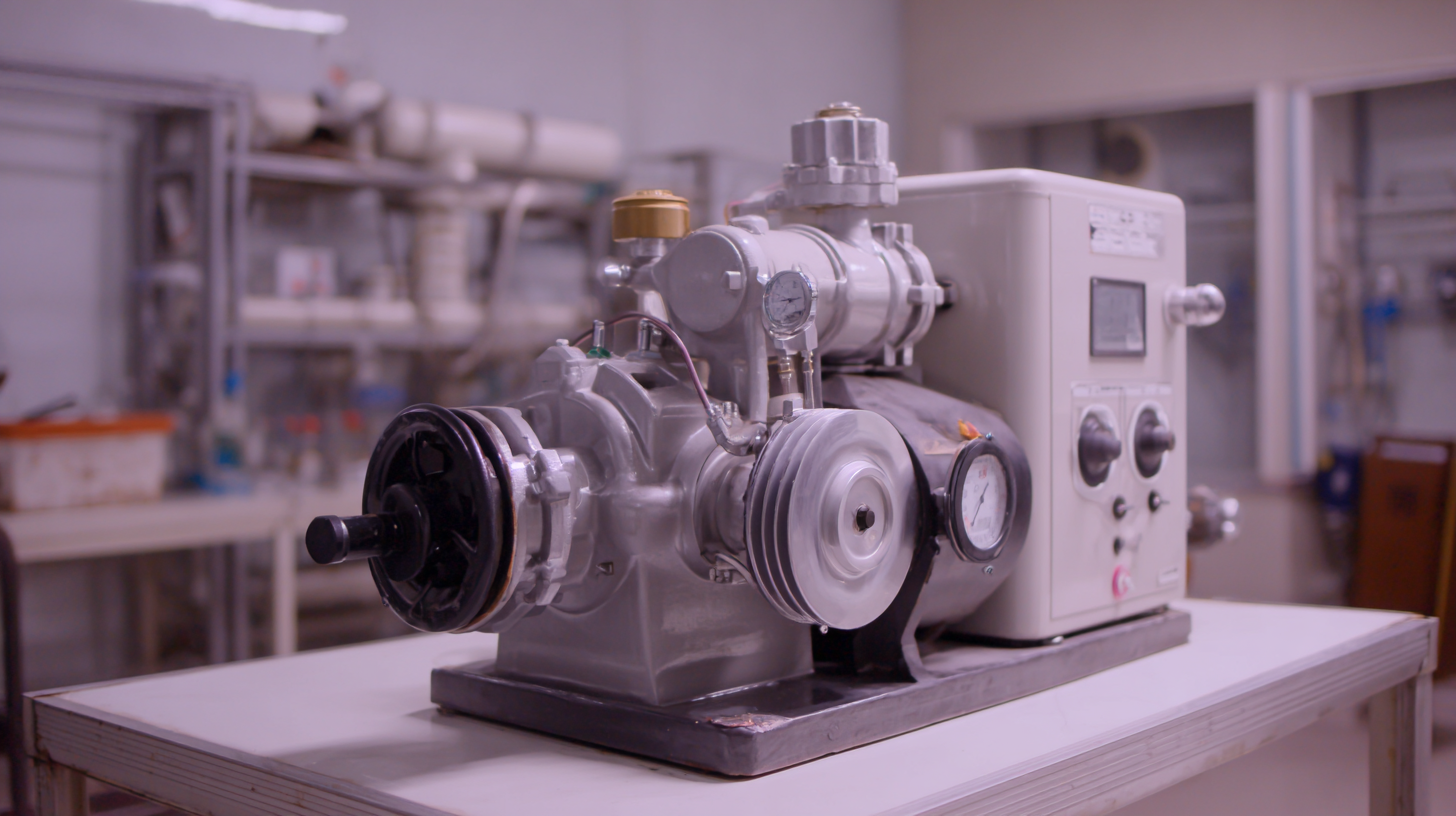

When considering the purchase of a suction pump, it's essential to conduct a thorough cost analysis that encompasses not only the initial acquisition price but also ongoing maintenance expenses. The initial investment can vary significantly based on pump type, capacity, and features, ranging from budget options to high-end industrial models. A buyer must assess their specific requirements to find a pump that offers the best value without compromising performance.
In addition to the purchase cost, maintenance is a critical aspect that should not be overlooked. Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and efficiency of a suction pump, which can translate to cost savings over time. Maintenance expenses may include routine inspections, parts replacement, and potential repairs. By budgeting adequately for both the purchase and anticipated maintenance costs, users can avoid unexpected financial burdens and maximize the utility of their suction pump investment. Ultimately, diligent financial planning enables users to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
sale@harbertpump.com,
sale@harbertpump.com,
sale@harbertpump.com,
sale@harbertpump.com,
sale@harbertpump.com